Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by death of motor neurons. To date, neither etiology nor pathogenesis of ALS is clear, which leads to the absence of an effective treatment strategy. The genetic cause of the disease confirmed in 5% of the cases; however, sporadic and hereditary forms share the molecular peculiarities of the disease development. Animal models obtained through the years did not help to clarify the details of ALS initiation and propagation due to incomplete reproduction of the disease pathogenesis. To unravel processes that are leading to motor neuron degeneration, we obtained IPSCs from a patient with the hereditary form of ALS with Asp90Ala mutation in the SOD1 gene which supposedly leads to misfolding and aggregation of SOD1 protein. Alongside with C9ORF72 hexanucleotide expansion and TDP-43 mutations, SOD1 mutations are the most common among patients with hereditary ALS. The results obtained from ALS iPSCs-derived motor neurons can be translated on other hereditary forms of ALS as well as on the non-hereditary (sporadic).
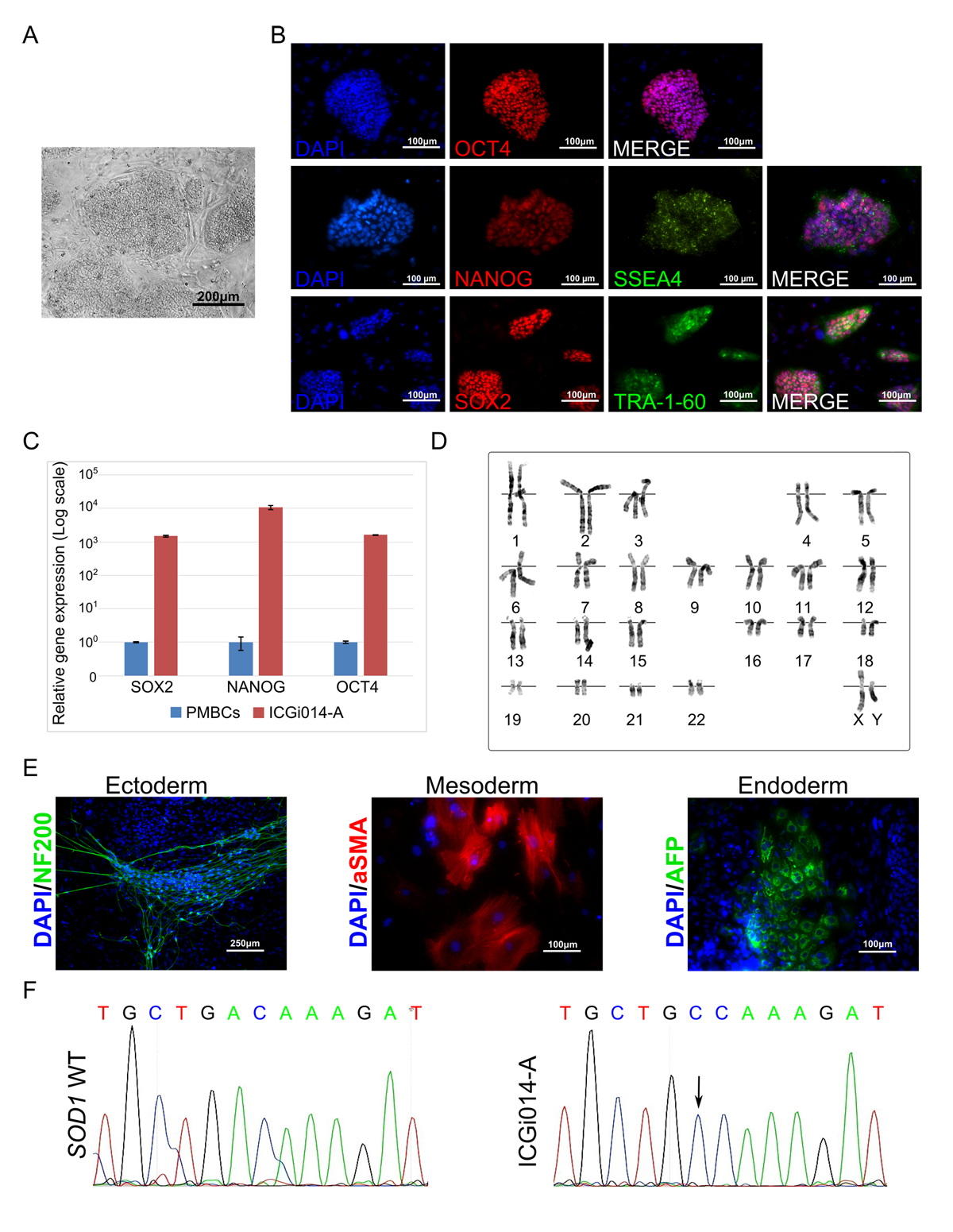
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by death of motor neurons. To date, neither etiology nor pathogenesis of ALS is clear, which leads to the absence of an effective treatment strategy. The genetic cause of the disease confirmed in 5% of the cases; however, sporadic and hereditary forms share the molecular peculiarities of the disease development. Animal models obtained through the years did not help to clarify the details of ALS initiation and propagation due to incomplete reproduction of the disease pathogenesis. To unravel processes that are leading to motor neuron degeneration, we obtained IPSCs from a patient with the hereditary form of ALS with Asp90Ala mutation in the SOD1 gene which supposedly leads to misfolding and aggregation of SOD1 protein. Alongside with C9ORF72 hexanucleotide expansion and TDP-43 mutations, SOD1 mutations are the most common among patients with hereditary ALS. The results obtained from ALS iPSCs-derived motor neurons can be translated on other hereditary forms of ALS as well as on the non-hereditary (sporadic).
