Duchenne muscular atrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe and rapidly progressive hereditary muscular disease with X-linked recessive inheritance, occurring mainly in males. A complete loss of dystrophin resulted from out-of-frame deletion mutations in the DMD gene leads to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. DMD induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are a suitable cell model to study muscle development and disease mechanisms underlying muscular dystrophy and to screen novel compounds with potential therapeutic effects. We generated iPSCs from a DMD patient with mutation c.2950-1G>C in the 3ʹ splice acceptor site of 22 intron of the DMD gene using non-integrating episomal plasmid vectors. The obtained iPSC lines showed ESC-like morphology, expression pluripotency markers, displayed a normal karyotype and possessed trilineage differentiation potential.
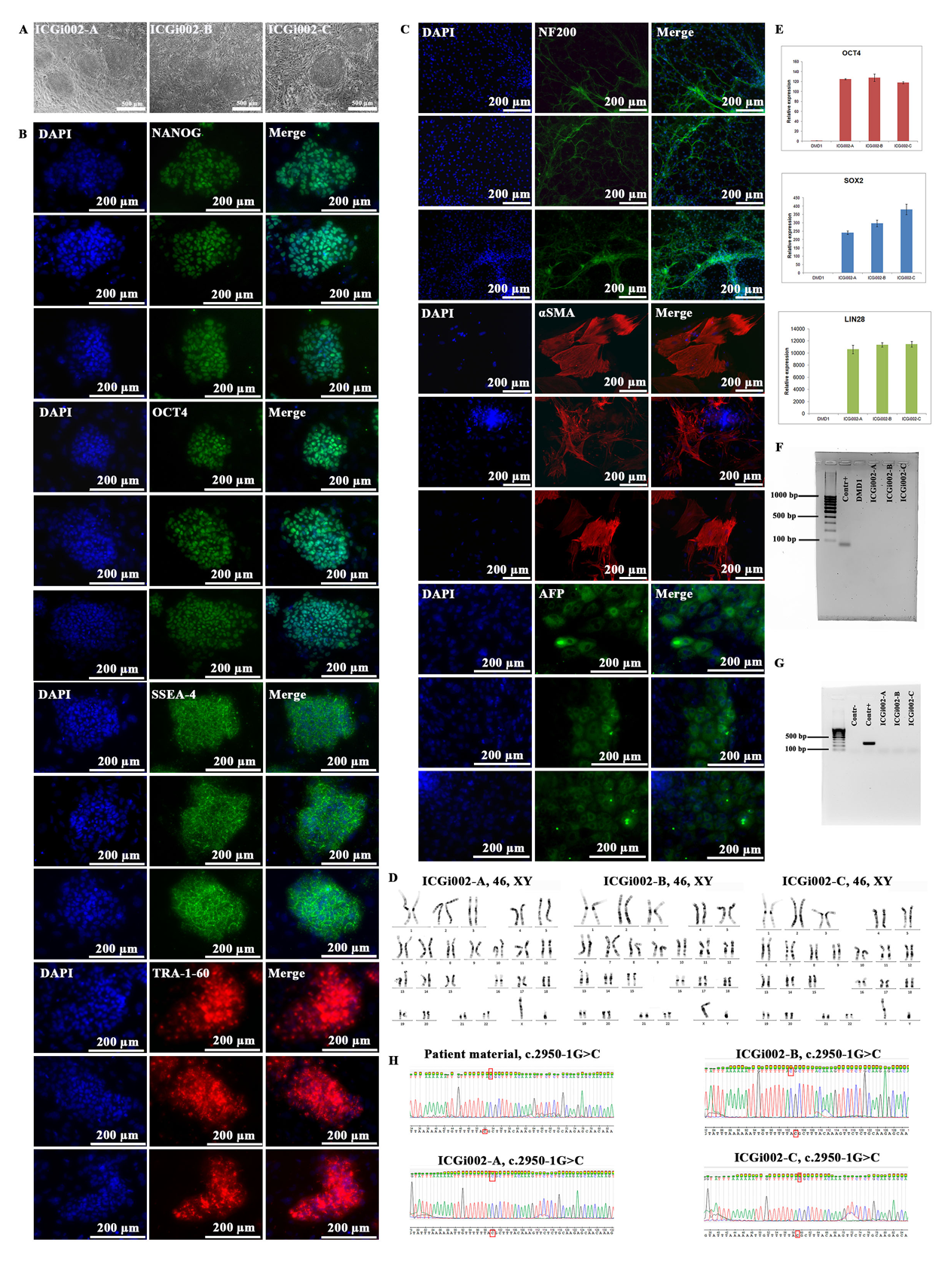
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe and rapidly progressive hereditary muscular disease with X-linked recessive inheritance, occurring mainly in males. A complete loss of dystrophin resulted from out-of-frame deletion mutations in the DMD gene leads to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. DMD induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are a suitable cell model to study muscle development and disease mechanisms underlying muscular dystrophy and to screen novel compounds with potential therapeutic effects. We generated iPSCs from a DMD patient with mutation c.2950-1G>C in the 3ʹ splice acceptor site of 22 intron of the DMD gene using non-integrating episomal plasmid vectors. The obtained iPSC lines showed ESC-like morphology, expression pluripotency markers, displayed a normal karyotype and possessed trilineage differentiation potential.
