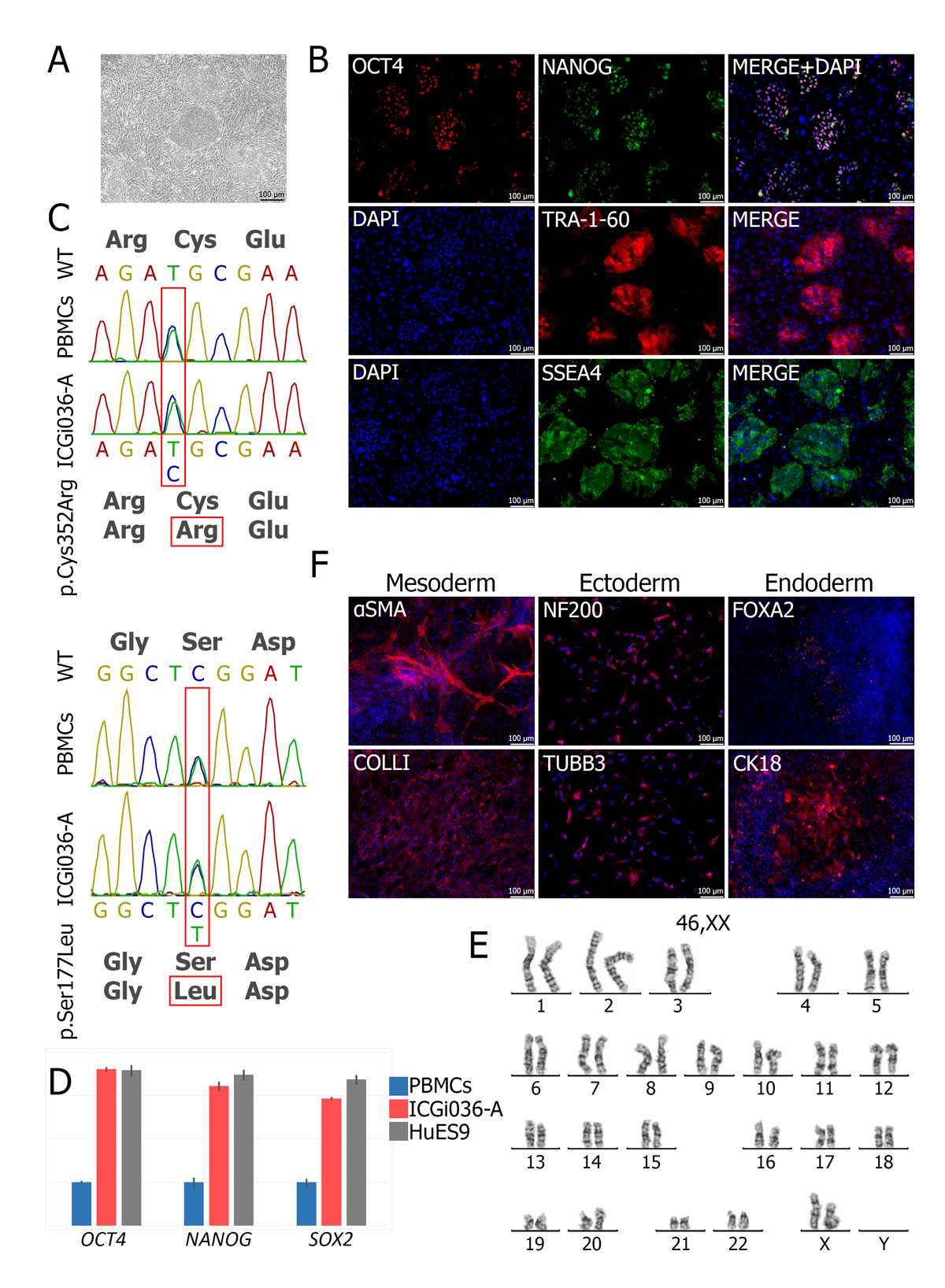
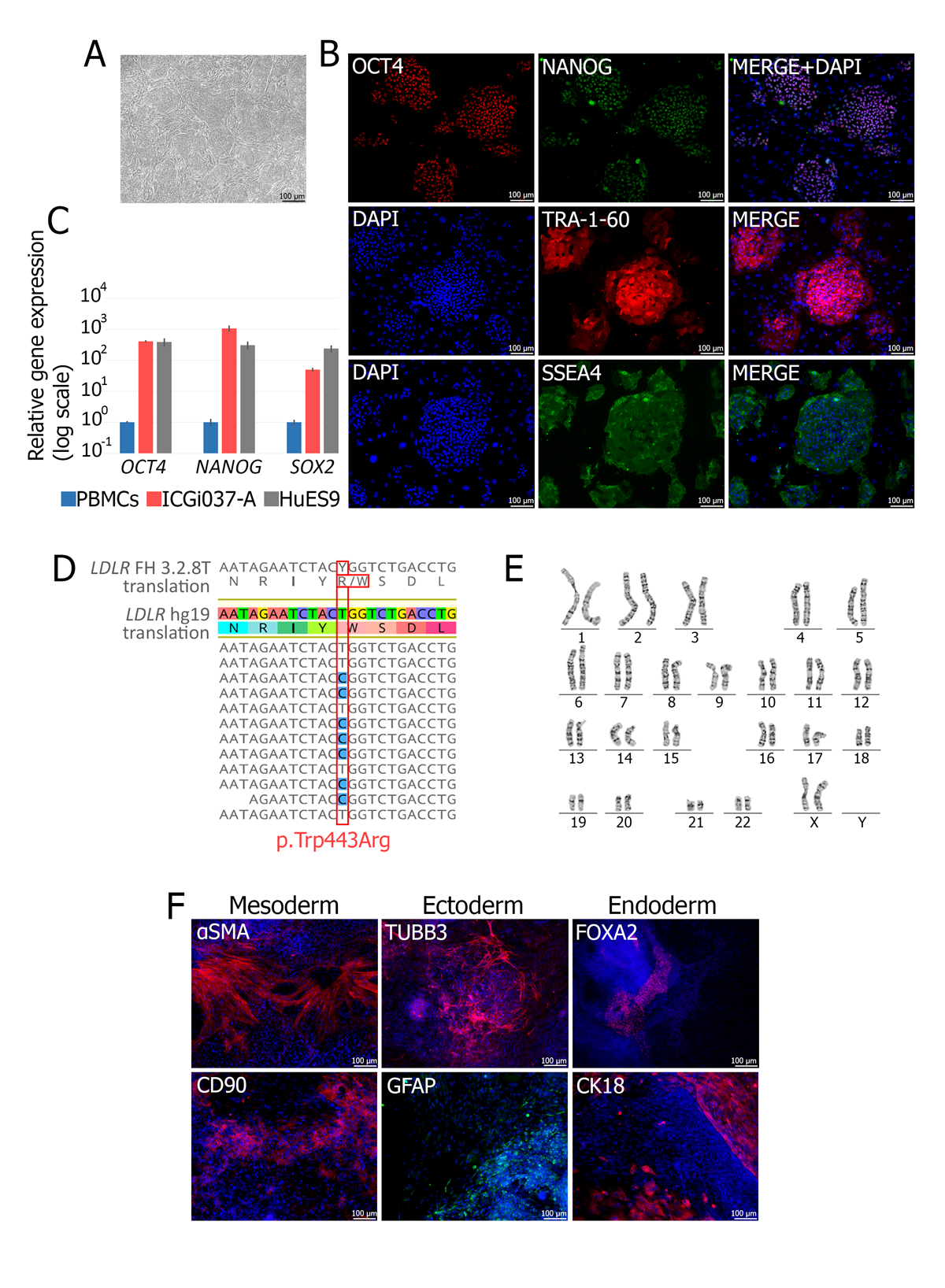
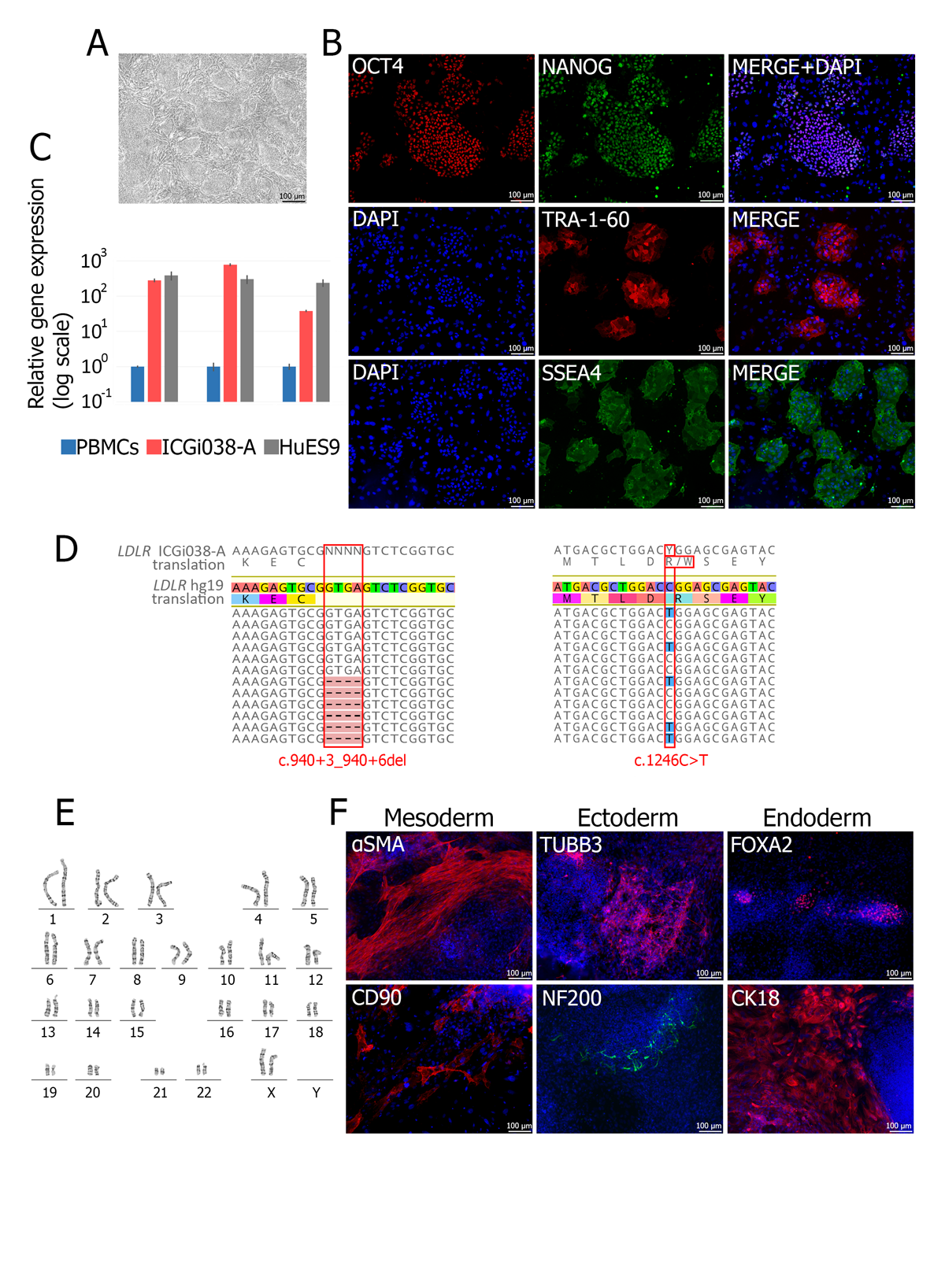
Familial hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a monogenic disease, leading to atherosclerosis due to a high level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Most cases of the disease are based on pathological variants in the LDLR gene. Available treatments are effective not for all LDLR mutations. The development of cellular models for FH is an important direction for creating new approaches to atherosclerosis treatment.
This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant № 21-15-00065).