Huntington’s disease
Isogenic HD model
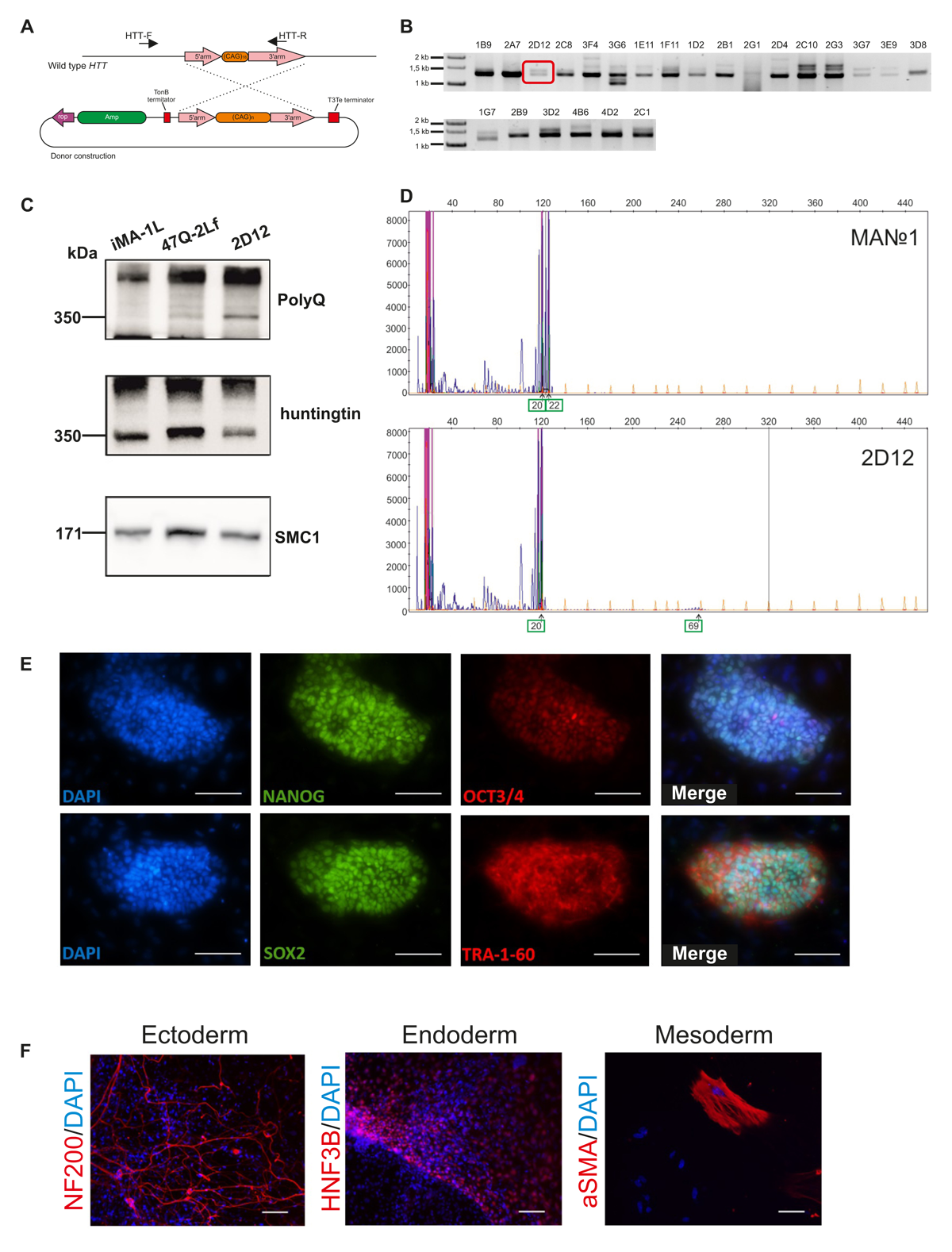
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a severe neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG triplet expansion in the first exon of the HTT gene. Here we generated isogenic iPSC-based HD model by introducing 69 CAG triplets into HTT through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homologous recombination. The obtained isogenic cell system can serve as a valuable model for the investigation into various parameters of HD and for screening of potential drugs without worries about background-related variability.
Isogenic HD model
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a severe neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG triplet expansion in the first exon of the HTT gene. Here we generated isogenic iPSC-based HD model by introducing 69 CAG triplets into HTT through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homologous recombination. The obtained isogenic cell system can serve as a valuable model for the investigation into various parameters of HD and for screening of potential drugs without worries about background-related variability.
