Huntington’s disease
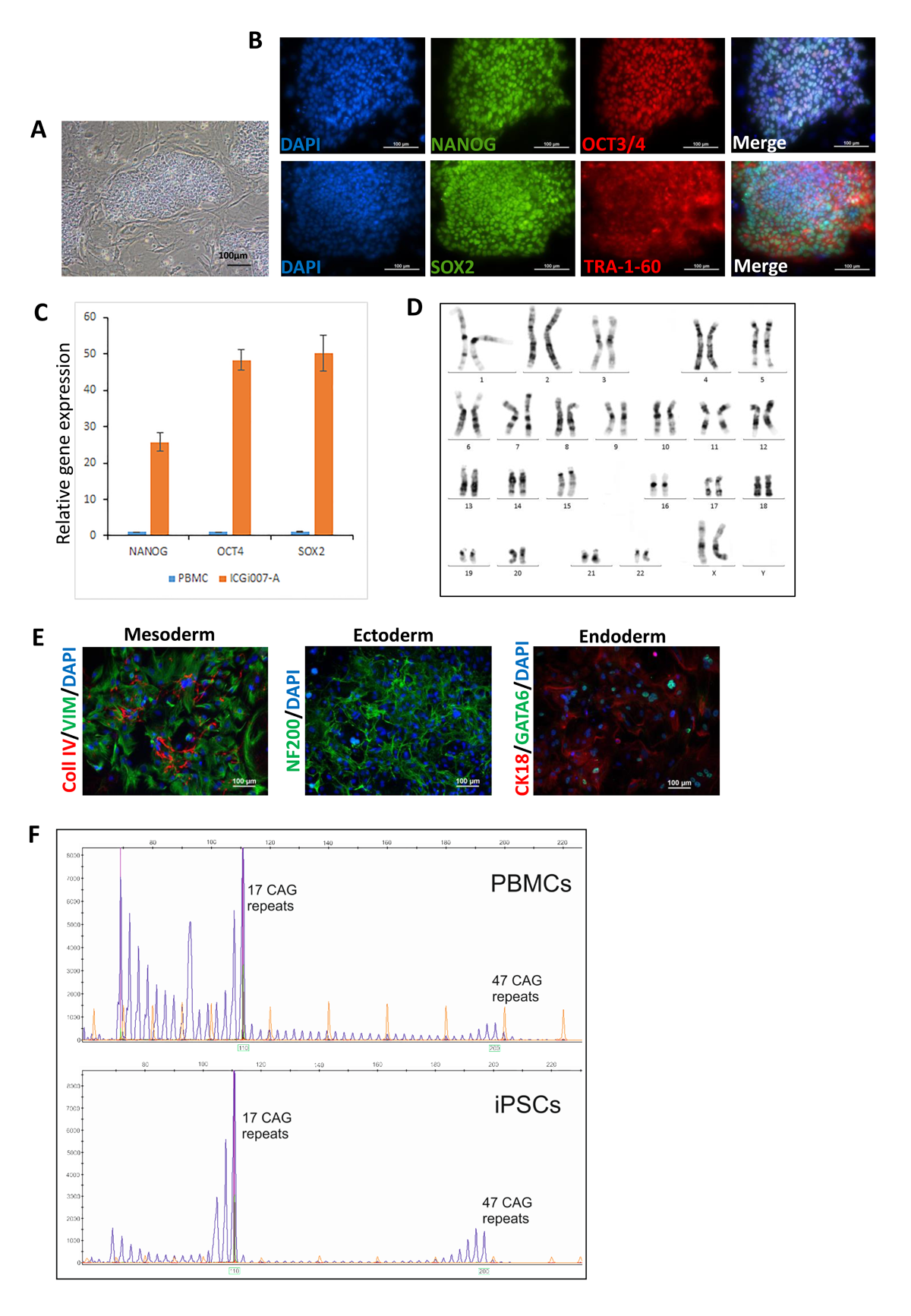
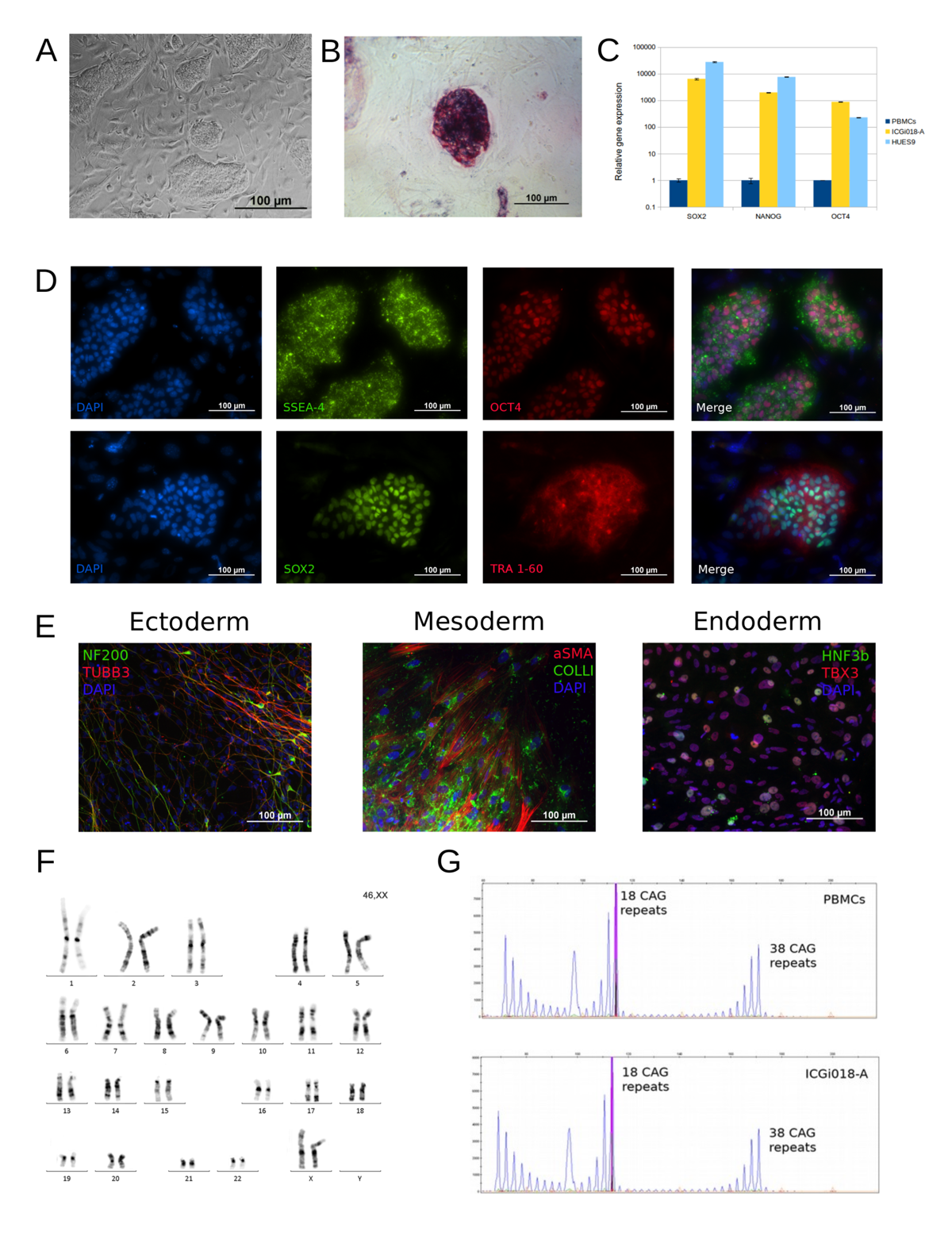
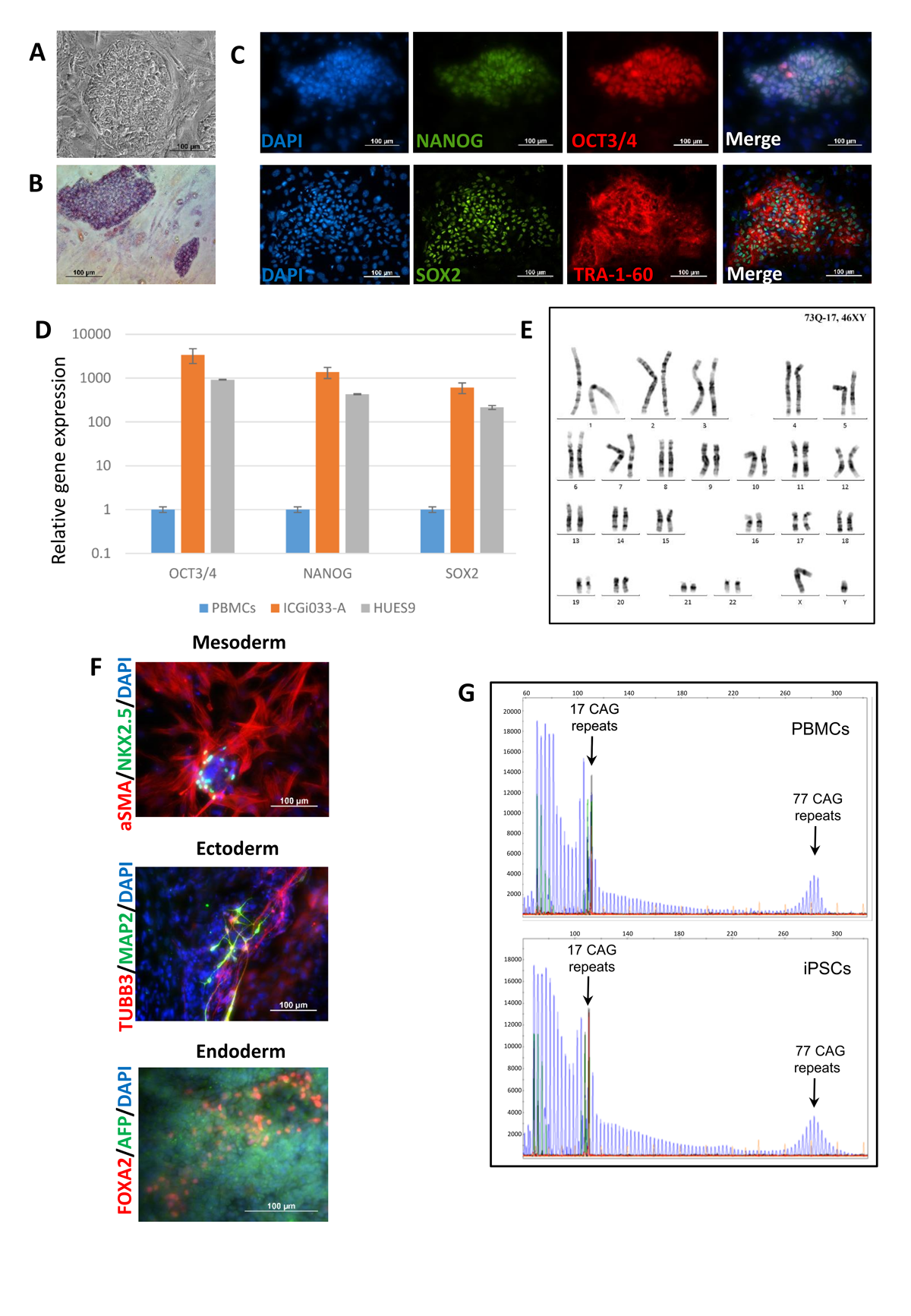
Huntington’s disease (HD) human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) represent a useful and valid model for the disease study (molecular mechanisms, large-scale drug screening, and toxicological studies). iPSC lines ICGi007-A (https://hpscreg.eu/cell-line/ICGi007-A), ICGi018-A (https://hpscreg.eu/cell-line/ICGi018-A) and ICGi033-A (https://hpscreg.eu/cell-line/ICGi033-A) from HD patients with 47,38 and 77 CAG triplets respectively in the HTT gene were generated from blood mononuclear cells by non-integrating episomal vectors. The iPSC lines retained the mutation, expressed pluripotency markers, had a normal karyotype and displayed in vitro differentiation to the cell types of the three germ layers.